Understanding the Spanish Verb Chart: Ar, Er, Ir
When learning Spanish, one of the most challenging aspects is mastering the conjugation of verbs. Spanish verbs are divided into three groups based on the ending of their infinitive forms: ar, er, and ir. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of these verb charts, providing you with a comprehensive guide to help you navigate through the complexities of Spanish verb conjugations.
What are Ar, Er, and Ir Verbs?

Ar, er, and ir verbs are the three primary verb groups in Spanish. They are characterized by their respective endings in the infinitive form. For instance, verbs ending in -ar, -er, and -ir belong to these groups, respectively. Understanding the differences between these verb groups is crucial for proper conjugation and usage.
Ar Verbs
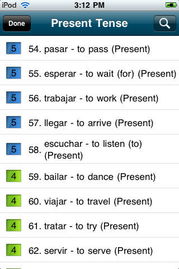
Ar verbs are the most common group in Spanish. They are characterized by their -ar ending in the infinitive form. Some examples of ar verbs include “hablar” (to talk), “comer” (to eat), and “vivir” (to live). Conjugating ar verbs is relatively straightforward, as they follow a consistent pattern. Here’s a brief overview of the conjugation chart for ar verbs:
| Subject | Present Tense | Past Tense |
|---|---|---|
| yo | hablo | habl茅 |
| t煤 | hablas | hablaste |
| 茅l/ella/usted | habla | habl贸 |
| nosotros/nosotras | hablamos | hablamos |
| ustedes | hablan | hablaron |
As you can see, the conjugation pattern for ar verbs is consistent across all subjects. However, it’s important to note that some ar verbs have irregular forms, such as “ir” (to go), which is an exception to the rule and requires special attention.
Er Verbs

Er verbs are the second most common group in Spanish. They are characterized by their -er ending in the infinitive form. Some examples of er verbs include “ser” (to be), “ir” (to go), and “ver” (to see). Conjugating er verbs is similar to ar verbs, but with a few exceptions. Here’s a brief overview of the conjugation chart for er verbs:
| Subject | Present Tense | Past Tense |
|---|---|---|
| yo | soy | fu铆 |
| t煤 | eres | fuiste |
| 茅l/ella/usted | es | fue |
| nosotros/nosotras | somos | fuimos |
| ustedes | son | fueron |
Like ar verbs, er verbs have a consistent conjugation pattern across all subjects. However, some er verbs, such as “ir,” have irregular forms that require special attention.
Ir Verbs
Ir verbs are the least common group in Spanish. They are characterized by their -ir ending in the infinitive form. Some examples of ir verbs include “ir” (to go), “venir” (to come), and “irse” (to go away). Conjugating
