Mediview AR: A Revolutionary Leap in Medical Visualization
Immersive technology has been making waves across various industries, and the medical field is no exception. One such innovation that has been gaining traction is Mediview AR, a cutting-edge augmented reality (AR) platform designed to revolutionize the way medical professionals visualize and interact with patient data. In this detailed exploration, we will delve into the various dimensions of Mediview AR, showcasing its capabilities and potential impact on healthcare.
Understanding Mediview AR
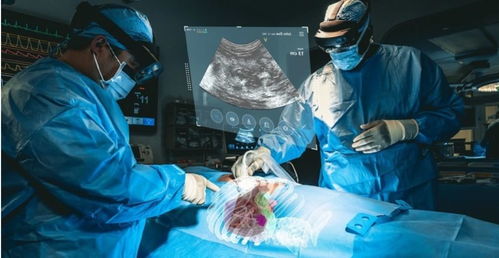
Mediview AR is an AR platform that allows medical professionals to overlay 3D medical images onto the real world. By using a smartphone or tablet, users can view and manipulate these images in real-time, providing a more intuitive and interactive way to understand complex medical conditions.
How Mediview AR Works
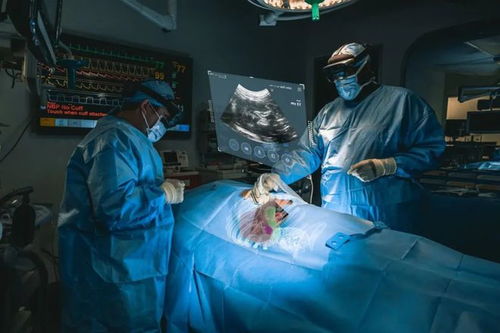
Mediview AR utilizes a combination of advanced algorithms and hardware to create a seamless AR experience. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
-
Image Acquisition: Medical professionals upload patient data, such as CT or MRI scans, to the Mediview AR platform.
-
3D Reconstruction: The platform then processes the data, converting it into a 3D model that can be viewed in AR.
-
Real-Time Overlay: Using a smartphone or tablet, users can view the 3D model overlaid onto the real world, allowing for a more intuitive understanding of the patient’s condition.
-
Interactivity: Users can manipulate the 3D model, zoom in and out, rotate it, and even share it with colleagues for collaborative analysis.
Applications of Mediview AR
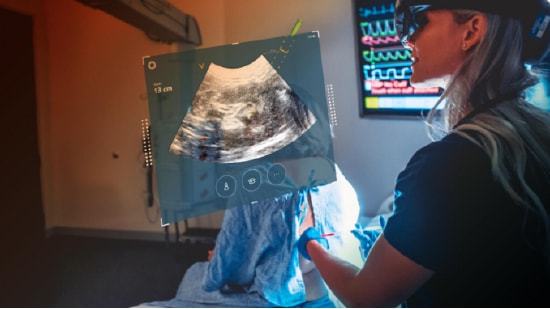
Mediview AR has a wide range of applications across various medical fields. Here are some of the key areas where it can make a significant impact:
1. Radiology
In radiology, Mediview AR can help radiologists visualize complex medical conditions more effectively. By overlaying 3D images onto the patient’s body, radiologists can better understand the location and extent of abnormalities, leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
2. Surgery
During surgical procedures, Mediview AR can provide surgeons with real-time, 3D visualizations of the patient’s anatomy. This can help surgeons navigate complex surgical scenarios, reduce the risk of complications, and improve patient outcomes.
3. Education
Mediview AR can be a valuable tool for medical students and educators. By providing an interactive and immersive learning experience, students can better understand complex medical concepts and procedures.
4. Telemedicine
In telemedicine, Mediview AR can help healthcare providers remotely visualize patient data, enabling more accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
Benefits of Mediview AR
Mediview AR offers several benefits over traditional 2D imaging methods:
-
Improved Visualization: The 3D nature of Mediview AR provides a more intuitive and comprehensive understanding of patient data.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Users can easily share and manipulate 3D models, facilitating collaboration among medical professionals.
-
Reduced Errors: The ability to visualize complex medical conditions in real-time can help reduce errors in diagnosis and treatment.
-
Cost-Effective: Mediview AR can be accessed using existing hardware, such as smartphones and tablets, making it a cost-effective solution for healthcare providers.
Real-World Examples
Several healthcare institutions have already implemented Mediview AR into their practices, showcasing its potential impact on the medical field. Here are a few examples:
| Institution | Application | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Johns Hopkins Hospital | Neurosurgery | Improved preoperative planning and reduced complications |
| University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) | Cardiology | Enhanced visualization of cardiac anatomy and improved treatment planning |
| University of Miami | function pinIt() { var e = document.createElement('script'); e.setAttribute('type','text/javascript'); e.setAttribute('charset','UTF-8'); e.setAttribute('src','https://assets.pinterest.com/js/pinmarklet.js?r='+Math.random()*99999999); document.body.appendChild(e); }
